 |
Home | Documentation |
The iOS Plugin
updated Wed Apr 8 2020 by Robert van Engelen
|
 |
Home | Documentation |
The iOS Plugin
updated Wed Apr 8 2020 by Robert van Engelen
|
By Bethany Sanders, Robert van Engelen, Ning Xie, and Wei Zhang
Consuming Web services on iOS (iPhone and iPad) platforms is increasingly in demand today. Xcode does not offer built-in tools that make consuming XML Web services easy. This means that detailed knowledge of XML processing is required to send SOAP/XML and XML REST requests to the Web services and parse the XML response. By contrast, the gSOAP toolkit offers an automated XML data binding toolkit for C and C++ to develop SOAP/XML Web services and clients. You can also use the iOS plugin to consume XML-RPC and JSON Web services with the XML-RPC & JSON/JSON-Path plugin for gSOAP. The plugin makes it easy to consume Web services on iOS platforms, such as iPhone and iPad. Moreover, the plugin takes advantage of iOS network connectivity by supporting 3G/4G/LTE and wifi.
To use the iOS plugin for development of client applications on iOS platforms, register the plugin with the gSOAP engine context as follows:
When coding in C++, it is recommended to generate C++ proxy classes with soapcpp2 option -j which are then used to instantiate proxy objects that manage the gSOAP engine context to register with the plugin as follows:
There are no other plugin API calls necessary to make a Web service client application work with iOS. This means that you can develop iOS apps that consume complex SOAP/XML, XML REST, and JSON Web services.
To start building Web services client applications for iPhone and/or iPad with gSOAP, you will need:
Developing Web services client applications on iOS is no different than developing these applications on another OS with gSOAP when you use this iOS Plugin.
The steps to create a client application on iOS:
All of the source code files should be of type Objective C++ source. Mixing C files with C++ files will cause errors. Rename .c files to .cpp files as necessary.
The interaction between the client and the Web serviceserver can be controlled by specifying the cache policy. To specify the cache policy, use the API function soap_ios_setcachepolicy(struct soap *soap, unsigned int policy). This API function cannot be called before the plugin is registered.
The available cache policies that can be specified are:
The default cache policy is NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy.
The timeout of a network connection can be specified using the API function soap_ios_settimeoutinterval(struct soap *soap, double seconds):
The default timeout is 60 seconds.
To support authentication when access is denied (HTTP 401 error) when the client tries to connect, enable HTTP authentication as follows.
Basic authentication is simply enabled at the client-side by setting the soap.userid and soap.passwd strings to a username and password, respectively:
When using a generated C++ proxy class:
Make sure to never use Basic authentication without HTTPS. HTTPS must be used to ensure that Basic authentication is secure.
This section introduces four examples to demonstrate the development of client applications consuming Web services on iOS platforms, such as iPhone and iPad, by using the gSOAP tools and the iOS plugin.
The first example Simple Calculator Example (C++) is a basic calculator client app. The second example GeoIPService Example (C++) is a web service that locates the country of a certain IP Adress. The third example Weather Example (C++) returns weather results for well-known US cities, and the fourth example Air Example (C++) shows information on every airport within a given country.
We assume you already have had some experience developing applications for iPhone and iPad using Xcode with iOS SDK installed. Experience is not required to read on, but helpful in case you get lost in the details of the Xcode iOS SDK.
General recommendations:
This example shows you how to develop a client application in C++ using gSOAP and the ios plugin, which consumes a simple calculator service on iOS using gSOAP. The simple calculator service was developed and deployed as a demo to get started with gSOAP. The gSOAP Calculator Service provides several operations such as add, sub, mul, div etc. In this example, we use the operation add as a demo. Other operations are applied in a similar way. The wsdl file for this service can be obtained at the following link:
http://www.genivia.com/calc.wsdl
The Xcode project for this example can be found in gsoap/ios_plugin/examples/calc.
The gsoap/ios_plugin/examples/calc directory already contains calc.h so you can skip this step.
To generate codes for the calculator Web service, we first run the wsdl2h tool from the command line on the URL of the WSDL and use option -o to specify the output file (Alternatively, you can download the calc.wsdl and use the local file instead of the URL):
wsdl2h -o calc.h http://www.genivia.com/calc.wsdl
This generates the calc.h service definition header file with service operation definitions and types for the operation's data. By default, gSOAP assumes you will use C++ with STL.
We have not yet generated the stubs for the API. To do so, run the soapcpp2 compiler:
soapcpp2 -CL -I$GSOAP_HOME/import calc.h
Option -CL indicates client-side only files (soapcpp2 generates both client and server stubs and skeletons by default). This generates a number of source files for client application development. We do not have to generate a proxy class in this example because it does not use a Proxy class.
Launch Xcode, create a Single View-based Application project and name it Calc. Open the ViewController.xib (main storyboard) file in the Interface Builder. Double-click on the View item and populate it with the views listed below and shown in Figure 1:
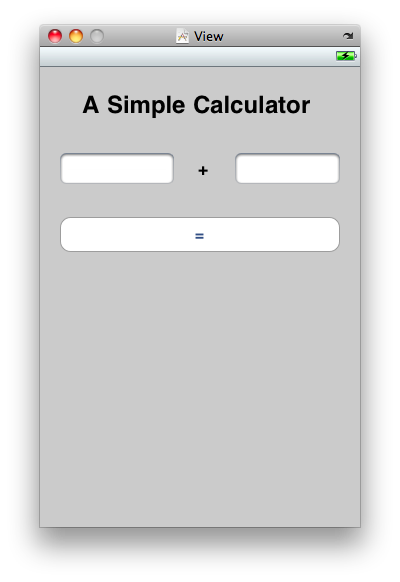
In Xcode, edit the file ViewController.h to make it look like the following:
Link the op1 and op2 to the two Text Fields and delegate the button action to method buttonPressed.
In Xcode, edit the file info.plist to make it look like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>
<key>CFBundleDevelopmentRegion</key>
<string>en</string>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>$(EXECUTABLE_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleSignature</key>
<string>????</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1</string>
<key>LSRequiresIPhoneOS</key>
<true/>
<key>UILaunchStoryboardName</key>
<string>LaunchScreen</string>
<key>UIMainStoryboardFile</key>
<string>Main</string>
<key>UIRequiredDeviceCapabilities</key>
<array>
<string>armv7</string>
</array>
<key>UISupportedInterfaceOrientations</key>
<array>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeLeft</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeRight</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
These changes ensure that you can access the web services despite the added layer of protection (App Transport Security).
Add the source files soapC.cpp, soapClient.cpp, soapH.h, and soapStub.h generated in Step 1 of this tutorial to the project. Also add files stdsoap2.h and stdsoap2.cpp to the project from gSOAP package as well as the iOS plugin files gsoapios.h and gsoapios.mm.
Once all of your files have been added to the project, ensure they are all of type "Objective C++ Source". This ensures that there will be no issues with mixing Objective C and C++ code.
Firstly, edit file main.mm to import the file calc.nsmap. Link errors may arise without importing this XML namespace mapping table.
Then, implement the source file ViewController.mm as the following:
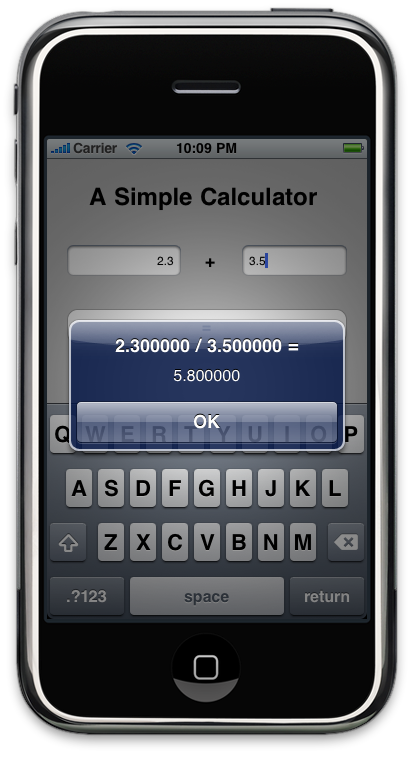
A screen snapshot of the client is shown in Figure 2.
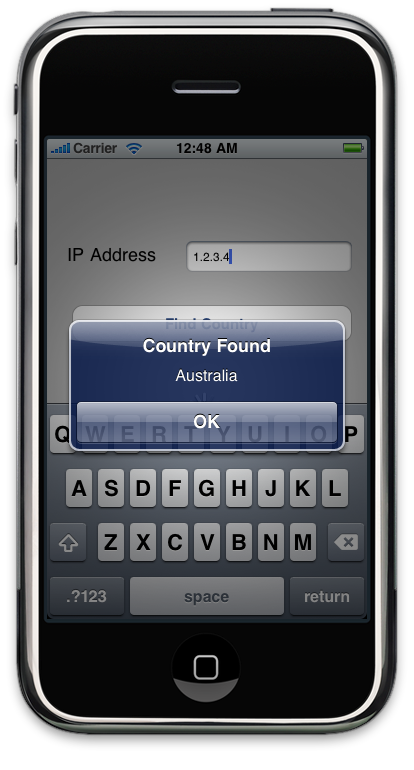
GeoIPService is a live SOAP Web service that enables you to look up countries by IP address or by Context.
This example shows you how to develop a client application in C++ using gSOAP and the ios plugin, which consumes the GeoIPService on iOS using gSOAP. The WSDL file for this service can be downloaded at the following link:
http://www.webservicex.net/geoipservice.asmx?WSDL
It is crucial to follow these directions in order for your app to work:
The Xcode project for this example can be found in gsoap/ios_plugin/examples/GeoIPService.
To generate codes for the GeoIPService Web service, we first run the wsdl2h tool from the command line on the URL of the WSDL and use option -o to specify the output file (alternatively, you can download the GeoIPService.wsdl file and use the local file instead of the URL):
wsdl2h -o GeoIPService.h -Ngeoip 'http://www.webservicex.net/geoipservice.asmx?WSDL'
This generates the GeoIPService.h service interface header file with service operation definitions and types for the operation's data. By default, gSOAP assumes you will use C++ with STL.
To generate the stubs for the C++ proxy classes, run the soapcpp2:
soapcpp2 -j -CL -I$GSOAP_HOME/import GeoIPService.h
Option -j tells the compiler to generate the C++ proxy class and option -CL indicates client-side only files (soapcpp2 generates both client and server stubs and skeletons by default). Option -I is needed to import the stlvector.h file from the import directory in the gSOAP package to support serialization of STL vectors.
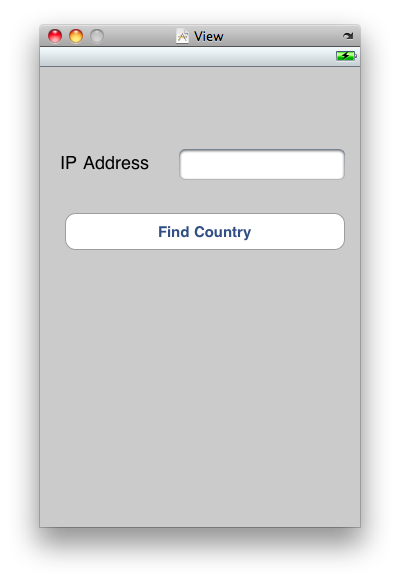
Create a Single View-based Application project and name it GeoIPService.Open the ViewController.xib (main storyboard) file in the Interface Builder. Double-click on the View item and populate it with the views listed below and shown in Figure 3:
In Xcode, edit the file ViewController.h to make it look like the following:
Set the ipAddress outlet and the buttonFindCountry:(id)sender method to delegate action of the button.
In Xcode, edit the file info.plist to make it look like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>
<key>CFBundleDevelopmentRegion</key>
<string>en</string>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>$(EXECUTABLE_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleSignature</key>
<string>????</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1</string>
<key>LSRequiresIPhoneOS</key>
<true/>
<key>UILaunchStoryboardName</key>
<string>LaunchScreen</string>
<key>UIMainStoryboardFile</key>
<string>Main</string>
<key>UIRequiredDeviceCapabilities</key>
<array>
<string>armv7</string>
</array>
<key>UISupportedInterfaceOrientations</key>
<array>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeLeft</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeRight</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
These changes ensure that you can access the web services despite the added layer of protection of App Transport Security).
Add the source files soapC.cpp, soapGeoIPServiceSoapProxy.cpp, soapGeoIPServiceSoapProxy.h, soapH.h, and soapStub.h generated in Step 1 of this tutorial to the project. Also add files stdsoap2.h and stdsoap2.cpp to the project from the gSOAP package and the iOS plugin files gsoapios.h and gsoapios.mm.
Once all of your files have been added to the project, ensure they are all of type "Objective C++ Source". This ensures that there will be no issues with mixing Objective C and C++ code.
Firstly, edit file main.mm to import the file GeoIPService.nsmap. Linking errors would arise without importing this XML namespace mapping table.
Then, implement the source file ViewController.mm as the following:
An image of the app is shown in Figure 4.
GlobalWeather is a live SOAP Web service that enables you to look up the Weather in popular cities around the world. For simplicity, this example is limited to cities in the United States. For some reason, some very popular cities are not supported by this web service. For example, no results for New York City will be returned. There is an error message within the app that shows whenever one of these cities is entered. Know that the error message is not an issue with the app you just built, but something that the web service itself does not provide.
This example shows how to develop a client application in C++ using gSOAP and the ios plugin, which consumes the Weather service on iOS using gSOAP. The WSDL file for this service can be downloaded at the following link:
http://www.webservicex.net/globalweather.asmx?WSDL
It is crucial to follow these directions in order for your app to work:
The Xcode project for this example can be found in gsoap/ios_plugin/examples/Weather.
To generate codes for the GeoIPService Web service, we first run the wsdl2h tool from the command line on the URL of the WSDL and use option -o to specify the output file (Alternatively, you can download the GlobalWeather.wsdl file and use the local file instead of the URL):
wsdl2h -o weather.h 'http://www.webservicex.net/globalweather.asmx?WSDL'
This generates the weather.h service definition header file with service operation definitions and types for the operation's data. By default, gSOAP assumes you will use C++ with STL.
Because we will be using the gSOAP DOM parser in this example, which is created in our program with xsd__anyType dom(ctx) to extract plain XML content received in string xmlmessage with xmlmessage >> dom, an additional step is necessary. Add the following line to the wsdl2h-generated airport.h file:
#import "dom.h"
To generate the stubs for the C++ proxy classes, run the soapcpp2 tool:
soapcpp2 -j -CL -I$GSOAP_HOME/import weather.h
Option -j tells soapcpp2 to generate the C++ proxy class and option -CL indicates client-side only files (soapcpp2 generates both client and server stubs and skeletons by default). Option -I is needed to import the stlvector.h file from the import directory in the gSOAP package to support serialization of STL vectors.
Create a Single View-based Application project and name it Weather. Open the ViewController.xib(main storyboard) file in the Interface Builder.Double-click on the View item and populate it with the views listed below and shown in Figure 3:
In Xcode, edit the file ViewController.h to make it look like the following:
Set the inputcity outlet and the buttonFindCountry:(id)sender method to delegate action of the button.
In Xcode, edit the file info.plist to make it look like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>
<key>CFBundleDevelopmentRegion</key>
<string>en</string>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>$(EXECUTABLE_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleSignature</key>
<string>????</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1</string>
<key>LSRequiresIPhoneOS</key>
<true/>
<key>UILaunchStoryboardName</key>
<string>LaunchScreen</string>
<key>UIMainStoryboardFile</key>
<string>Main</string>
<key>UIRequiredDeviceCapabilities</key>
<array>
<string>armv7</string>
</array>
<key>UISupportedInterfaceOrientations</key>
<array>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeLeft</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeRight</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
These changes ensure that you can access the web services despite the added layer of protection of App Transport Security).
Add the source files soapC.cpp, soapGloabalWeatherSoapProxy.cpp, soapGloabalWeatherSoapProxy.h, soapH.h, and soapStub.h generated in Step 1 of this tutorial to the project. Also add files stdsoap2.h and stdsoap2.cpp to the project from gsoap package and the iOS plugin files gsoapios.h and gsoapios.mm.
Once all of your files have been added to the project, ensure they are all of type "Objective C++ Source". This ensures that there will be no issues with mixing Objective C and C++ code.
Firstly, edit file main.mm to import the file GlobalWeatherSoap.nsmap. Linking errors would arise without importing this XML namespace mapping table.
Then, implement the source file ViewController.mm as the following, where we used the gSOAP domcpp tool with option -i on an example weather XML data file to produce DOM code to extract the XML data (see further below):
You will notice there is much more code in this example's ViewController.mm. This is because this web service stores the whole XML response within a string instead of appropriate variables. The dom parser can fix this situation so that you can still access your results without having to parse the XML yourself. The dom code in this example was generated via command line in UNIX. To do so, once you have dom executable in your working directory, just execute the command
./domcpp -i weather.xml
where weather.xml is a file that stores an example xml response. Option -i tells the domcpp tool to generate the code you need to parse your result. To obtain an example XML response, test the web service on http://www.webservicex.net/New/Home/ServiceDetail/56.
The domcpp tool is found in gsoap/samples/dom and should be built in that directory with:
make domcpp
Then move or copy the domcpp executable to use it for your projects.
For more information about domcpp, read XML DOM and XPath of the gSOAP documentation.
Airport Information Web Service is a live SOAP Web service that enables you to look up Airport Information of countries around the world. For some reason, some very well known countries are not supported by this web service. For example, no results for Russia will be returned. There is an error message within the app that shows whenever one of these countries is entered. Know that the error message is not an issue with the app you just built, but information that the web service itself does not provide.
This example shows how to develop a client application in C++ using gSOAP and the ios plugin, which consumes the Weather service on iOS using gSOAP. The WSDL file for this service can be downloaded at the following link: http://www.webservicex.net/airport.asmx?WSDL
It is crucial to follow these directions in order for your app to work:
The Xcode project for this example can be found in gsoap/ios_plugin/examples/Air.
To generate codes for the GeoIPService Web service, we first run the wsdl2h tool from the command line on the URL of the WSDL and use option -o to specify the output file (Alternatively, you can download the airport.wsdl file and use the local file instead of the URL):
wsdl2h -o airport.h 'http://www.webservicex.net/airport.asmx?WSDL'
This generates the airport.h service definition header file with service operation definitions and types for the operation's data. By default, gSOAP assumes you will use C++ with STL.
Because we will be using the gSOAP DOM parser in this example, which is created in our program with xsd__anyType dom(ctx) to extract plain XML content received in string xmlmessage with xmlmessage >> dom, an additional step is necessary. Add the following line to the wsdl2h-generated airport.h file:
#import "dom.h"
To generate the stubs for the C++ proxy classes, run the soapcpp2:
soapcpp2 -j -CL -I$GSOAP_HOME/import airport.h
Option -j tells the compiler to generate the C++ proxy class and option -CL indicates client-side only files (soapcpp2 generates both client and server stubs and skeletons by default). Option -I is needed to import the stlvector.h file from the import directory in the gSOAP package to support serialization of STL vectors.
Create a Single View-based Application project and name it Air. Open the ViewController.xib(main storyboard) file in the Interface Builder.Double-click on the View item and populate it with the views listed below and shown in Figure 3:
In Xcode, edit the file ViewController.h to make it look like the following:
Set the country_name and showResults outlets and the buttonFindCountry:(id)sender method to delegate action of the button.
In Xcode, edit the file info.plist to make it look like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>
<key>CFBundleDevelopmentRegion</key>
<string>en</string>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>$(EXECUTABLE_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>$(PRODUCT_NAME)</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleSignature</key>
<string>????</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1</string>
<key>LSRequiresIPhoneOS</key>
<true/>
<key>UILaunchStoryboardName</key>
<string>LaunchScreen</string>
<key>UIMainStoryboardFile</key>
<string>Main</string>
<key>UIRequiredDeviceCapabilities</key>
<array>
<string>armv7</string>
</array>
<key>UISupportedInterfaceOrientations</key>
<array>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeLeft</string>
<string>UIInterfaceOrientationLandscapeRight</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
These changes ensure that you can access the web services despite the added layer of protection of App Transport Security).
Add the source files soapC.cpp, soapairportSoapProxy.cpp, soapairportSoapProxy.h, soapH.h, and soapStub.h generated in Step 1 of this tutorial to the project. Also add files stdsoap2.h and stdsoap2.cpp to the project from the gSOAP package and the iOS plugin files gsoapios.h and gsoapios.mm.
Once all of your files have been added to the project, ensure they are all of type "Objective C++ Source". This ensures that there will be no issues with mixing Objective C and C++ code.
Firstly, edit file main.mm to import the file airportSoap.nsmap. Linking errors would arise without importing this XML namespace mapping table.
Then, we implement the source file ViewController.mm as the following, where we used the gSOAP domcpp tool with option -i on an example weather XML data file to produce DOM code to extract the XML data (see further below)
You will notice there is much more code in this example's ViewController.mm. This is because this web service stores the whole XML response within a string instead of appropriate variables. The dom parser can fix this situation so that you can still access your results without having to parse the XML yourself. The dom code in this example was generated via command line in UNIX. To do so, once you have dom executable in your working directory, just execute the command
./domcpp -i airPorts.xml
where airPorts.xml is a file that stores an example xml response. The option -i is what tells the dom tool to generate the code you need to parse your result. To obtain an example XML response, test the web service on http://www.webservicex.net/New/Home/ServiceDetail/20.
The domcpp tool is found in gsoap/samples/dom and should be built in that directory with:
make domcpp
Then move or copy the domcpp executable to use it for your projects.
For more information about domcpp, read XML DOM and XPath of the gSOAP documentation.